An arithmetic sequence is a sequence of numbers such that the difference between two consecutive terms is constant. The sequence
7, 13, 19, 25, 31, 37, 43, 59
is an example of an arithmetic sequence with first term 7, constant difference 6, and last term 49.
You have learned in that the formula for finding the nth term of the arithmetic sequence 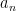 with first term
with first term  , and constant difference
, and constant difference 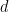 is given by
is given by
 .
.
In this post, we derive the formula for finding the sum of all the numbers in an arithmetic sequence. We take the specific example above and use Gauss’ method in finding the sum of the first 100 positive integers. Recall that in adding the first 100 integers, Gauss added the first integer to the last, the second integer to the second to the last, the third integer and the third to the last and so on. » Read more
,
, and
, its area
can be calculated using the Heron’s formula
