GeoGebra Essentials 8 – Graphs and their Properties
This is the eighth tutorial in the GeoGebra Essentials Series. If you are not familiar with GeoGebra, you may want to read the Introduction to GeoGebra post and earlier tutorials.
In the tutorial below, menu commands, located in the menu bar, are in brown bold text, and submenus are denoted by the > symbol. For example, Options>Labeling>New Points Only means, click the Options menu, choose Labeling from the list, then select New Points Only. The tool texts are colored orange. For example, New Point means the new point tool. Text that are to be typed in the input box are colored blue.
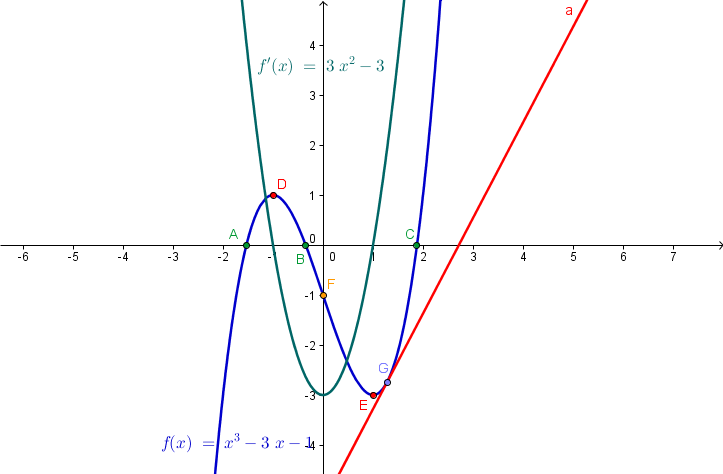
In this tutorial, we learn how to graph functions using GeoGebra. First, we graph a function, then determine its critical points (minimum, maximum, inflection point, roots) using GeoGebra keyboard commands. Then we get the derivative of the function. We also construct a point on the function and a line tangent through that point. We explore the characteristics of the tangent line in relation to the graph of the function and its derivative. The final output of our tutorial is shown above. » Read more