CaR Tutorial 2 – The MidSegment Theorem
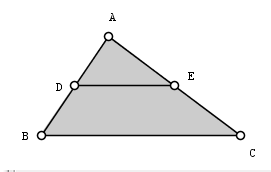
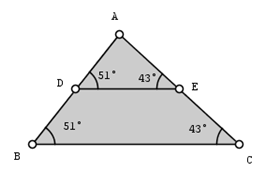
In the previous CaR tutorial, we constructed and isosceles triangle. In this tutorial we are going to explore the properties of the segment connecting the midpoints of its two sides. In this tutorial we are going to learn the following:
- use the move tool, triangle tool and segment tool
- find the midpoint of two a segment
- measure angles using the angle tool
- edit properties and reveal measures of angles and segments
Construction Steps