Milkshakes and Power Sets
In Milkshakes, Beads, and Pascal’s Triangles, we have talked about a systematic way of choosing a combination of objects from a larger number of objects. Let us recall the problem in the said post.
Issa went to a shake kiosk and want to buy a milkshake. The shake vendor told her that she can choose plain milk, or she can choose to combine any number of flavors in any way she wants. There are four flavors to choose from: Apple, Banana, Chico, and Durian. How many possible combination of flavors can Issa make?
In the problem, Issa can choose any number of flavors and any combination. She can choose plain milk, choose one flavor at a time, two flavors at a time, three flavors at a time, or four flavors at a time as shown in the table below (click the table to enlarge).
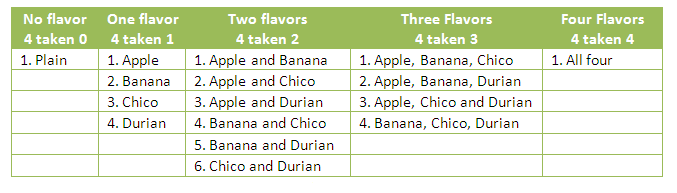
Notice that in writing the list, we have exhausted the number of subsets in a set with four elements. If we let a, b, c, and d stand for avocado, banana, chico, and durian, let them be members or a set and use the set notation, we can write the subsets as follows: » Read more